The SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) hierarchy helps large organizations to adopt Agile in the best way possible; it facilitates Decentralised Communication between teams and strongly links the business objectives with implementation execution.

Introduction
Agile adoption has transformed the ability of organizations to develop and deliver software solutions that yield business values, accommodate changing user needs and integrate customers’ perspectives. While Agile is most effective for small teams, the process of scaling Agile practices across a larger organization is fraught with challenges.
This is where the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) comes in as the solution to this challenge. SAFe helps companies integrate Agile into their structures, offering a formal framework which supports the collaboration of several teams, departments, and functions to deliver one vision.
In this article, we will learn about the SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) hierarchy and distinguish between levels and their roles, from teams to portfolios. This guide will explain the contents of SAFe framework levels, key roles in SAFe and how they interrelate.
CHECK OUT SAFe CERTIFICATION COURSES OFFERED BY VALUEX2
Overview of SAFe and Its Purpose
What is SAFe?
SAFe stands for Scaled Agile Framework, an extensive process management model to implement an Agile approach in large organizations, with numerous cross-functional teams and on massive projects.
It offers a framework and clear processes regarding work management, assignment coordination and integration with other teams to achieve business value and ongoing value delivery. The core of SAFe encompasses the Lean-Agile mindset, Lean manufacturing, Agile development, and a systems thinking approach.
It employs the use of DevOps practices to support the smooth delivery pipeline. It also prepares the minds of the company by cultivating customer-centricity which is the key driver of value delivery to the ultimate user.
How SAFe Fosters Large Teams and Complex Projects?
SAFe enhances the ability of organisations to address the interdependencies of teams and to direct them towards pursuing organisational goals. This structure outlines complex layers of operation ranging from teams to portfolios so that each works towards the business objectives.
The framework has four core values that guide its implementation:
Alignment: Safeguards that the multidimensional teams and departments of the organization operate in a coordinated manner to prevent status misunderstandings as well as overlapping tasks.
Built-in Quality: It surpasses quality at every process of development to ensure that what is delivered has the best quality.
Transparency: Facilitates awareness and transparency of work, to build confidence and foster sound decision-making throughout an organisation.
Program Execution: Broadly concerned with achieving valuable, excellent outcomes for positive program results by ensuring optimal program coordination and implementation.
By integrating these values properly, it becomes possible for the SAFe Agile Framework structure to remain an open system that can allow for adaptability within organizations while at the same time providing for well-proven and operational control. Thus, it is critical to evaluate the SAFe roles and their hierarchy since the idea is based on them.
Key Components of SAFe
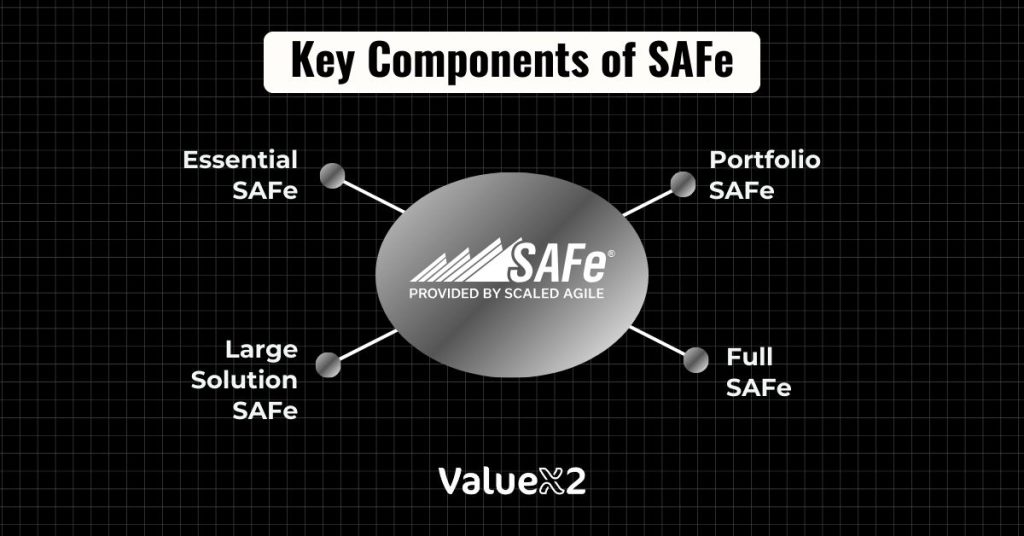
The SAFe (Scaled AgileFramework) hierarchy satisfies the different needs of an organization by providing scalability, flexibility and an organisational structure. It has four different arrangements to solve various issues associated with the enterprise scale Agile adoption. Let’s explore each in detail:
-
Essential SAFe
Essential SAFe is the fundamental structure of the SAFe Agile Framework structure. It is the least complex and many organizations that want to link Agile teams with organizational objectives and a corresponding backlog use it. It includes:
- Release trains to think flexibly for any number of teams called Agile Release Trains (ARTs).
- Professional resources such as the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Release Train Engineer.
- The actual planning effort, for instance, Program Increment (PI) planning is performed with high significance.
It is suitable for small and medium businesses or departments that have adopted Agile on a program level. It is indispensable as the initial point in comprehending the SAFe hierarchy described therein.
-
Large Solution SAFe
For organizations with complex, large portfolios involving multiple teams, Large Solution SAFe is a medium that provides coordination mechanisms. It includes:
- Support for other systems demanding multiple Agile Release Trains in their implementation.
- This is the case with roles like Solution Architects and Solution Management.
- The tools are related to managing dependencies between various teams and ARTs.
This is a level that meets the need for significant collaboration and is critical for the growth of Agile across large projects, illustrating the SAFe Agile framework components.
-
Portfolio SAFe
Portfolio SAFe is based on Agile methods and aims at implementing the organizational strategy. It introduces:
- An agile framework, such as Lean Portfolio Management (LPM) to invest resources efficiently.
- Sprint Owners who manage big plans or referred to as epics.
- Portfolio-level Kanban for managing work at a high level of the organization.
This configuration links the organization’s strategic plan with its operational implementation, which is why the portfolio scale must address SAFe framework levels.
-
Full SAFe
Of all the configurations, Full SAFe is the most extensive at featuring elements of the other configurations. It is ideal with regards to organizations that need to take Agile from one level of size to another. Full SAFe includes:
- Coordination at the team level, program level and portfolio level.
- Coordination between teams, workers, middle management and executives up to the enterprise level.
- Techniques for controlling the organization’s complexity in large organizations.
SAFe fully integrates the entire SAFe Agile framework structure and allows all stakeholders to work together efficiently and according to the plan.
Understanding SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) Hierarchy
The SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) hierarchy is set in such a way that there is effective working interface on the team, program, and organizational levels. It further divides into a set of clear and well-differentiated sub-layers with their associated roles and responsibilities and appropriate tools for the proper scaling of Agile practices. Let us dive deeper into the understanding of these SAFe framework levels.
Team Level
In essence, the organizational structure of the SAFe Agile Framework is underpinned by the Team Level that brings value to Agile teams incrementally.
Agile Teams
They are made up of variable sizes and create deliverables on a continuous basis in small cycles called Iterations. Using the Scrum and Kanban approaches, these teams continue to be effective and agile. While Scrum covers the work in ordered sprints, Kanban is based on continuous work and the visualization of tasks.
Key Roles
- Scrum Master: Helps the team to remain Agile compliant and can support in tasks such as team meetings such as stand-up meetings or retrospectives.
- Product Owner: Is involved in the establishment of priorities, within the product backlog that relates to the business objectives.
- Team Members: Engage developers, testers and designers who perform tasks to provide solutions.
Responsibilities and Tools
Each of them is responsible for iteration planning, performs daily meetings to share the progress, and holds retrospectives. These are backlogs, a task board, and Agile management software.
Program Level
The Program Level links up the Agile teams via an Agile Release Train program platform that is responsible for delivering discrete value in bi-iterations cycles.
Agile Release Train (ART)
The ART is the core of the discussed SAFe; it unites multiple Agile teams to cooperate closely. The work is centred on PI planning, a rhythmed activity to make sure everyone and everything is in phase.
Key Roles
- Release Train Engineer (RTE): Supports both ART processes and PI planning.
- Product Management: Outlines features, selection criteria, and conformity to current market trends.
- System Architect: Gives technical directions to guarantee that the design of the system is modular and sustainable.
Responsibilities and Outputs
The ART fulfils value in parts, addresses inter-team dependencies and actualizes program purpose.
Large Solution Level
The Large Solution Level analyzes those cases where multiple large systems and multiple ARTs are implicated.
When to Use Large Solution Level?
This level is used where a solution needs input from different ARTs or from external suppliers. It supports solutions that are more of system-of- systems.
Key Roles
- Solution Train Engineer: Concerts the management of several ARTs.
- Solution Management: More emphasis on capability definition and capability match with business requirements.
- Large Solutions Architect: Designs overarching technical solutions to many of the complex problems that organizations face.
Responsibilities
This level makes sure there is synergy amongst ARTs, conformity to business targets and handling of risk, making certain delivery associated with intricate systems.
Portfolio Level
The Portfolio Level links strategy and execution, and the SAFe roles and hierarchy are given at a more general level at this level.
Matching Business Strategies through Portfolios
At the Portfolio level, strategic goals are linked to operational implementation by value streams and Lean Portfolio Management.
Key Components
- Portfolio Vision: The framework used in determining decisions to be made in any organization.
- Value Streams: Identify who does what and how value flows through the organization.
- Lean Portfolio Management (LPM): Still, the corporate culture guarantees that organisational budgets and priorities correspond with business targets and objectives.
Key Roles
- Epic Owners: Help to run and coordinate big work efforts commonly referred to as initiatives or epics of the strategic plan.
- Lean Portfolio Manager: Is responsible for the creation of the budget and ensures that portfolio goals meet company goals.
Budgeting and Metrics
The portfolio level determines the resources to be employed based on needs and the use of KPIs to monitor in line with organizational objectives.
Enterprise Level
The Enterprise Level builds upon the SAFe Agile Framework structure to include the whole organisation cognising the Lean-Agile mindset.
Incorporation of SAFe with Organisation Strategic Targets
At this level, SAFe operates as one with an organizational strategy to provide agility and scalability across the organization.
Cultural Change and Leadership
Senior management has a responsibility of sustaining cultural change and managing the process of implementing Lean-Agile principles to support organisational agility.
Benefits of SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) Hierarchy
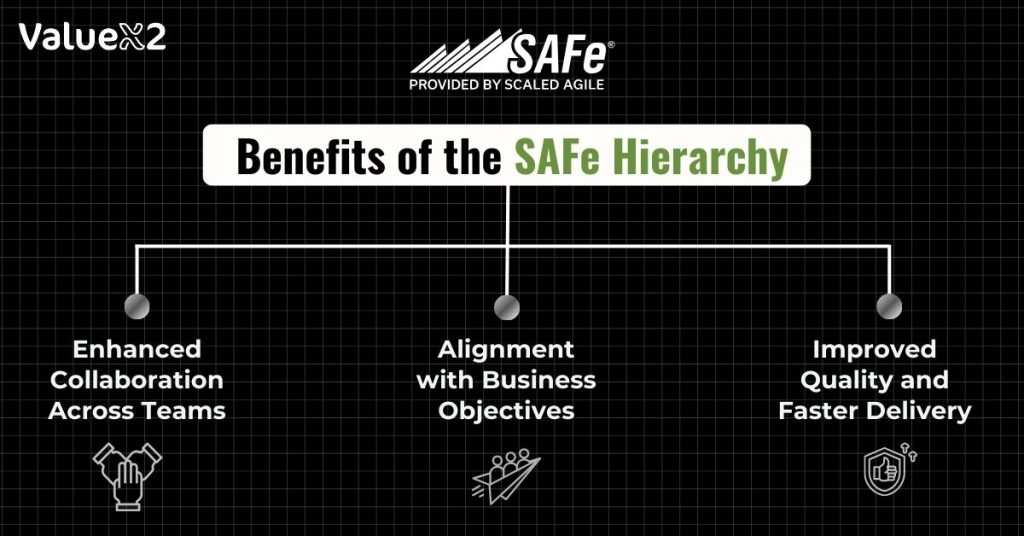
The SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) hierarchy provides the complete solution for the management of the Agile framework at large organizations. Additionally, the division of the system by levels and participants helps to avoid confusion in the work, achieve the necessary focus, and achieve the desired results.
1. Better Co-ordination with other Teams
The SAFe Agile Framework structure proactively establishes unity of communication and cooperation among various teams, departments, and other stakeholders. Another way through which the SAFe structure helps is by providing clearly defined roles and responsibilities within the organizational hierarchy further helping align all stakeholders in the organization towards the right objectives. There are no more silos between Agile teams, Solution level and Portfolio, all of them share trustful relationships and responsibilities.
2. Support for Business Goals
SAFe framework levels are one of the work’s main benefits; it effectively connects daily work with business goals. Thus, the strategic elements of the SAFe Agile Framework ensure the teams and programs are in synergy with the overall vision of an enterprise. It is therefore now easier for organizations to facilitate the alignment of their strategies and to see results being achieved on the ground.
3. Better Quality and Shorter Time Frame
Prominent in the SAFe framework described here are iteration, integration, and testing. These practices result in better quality of the particular product and fast delivery. Using ARTs and PIs, the teams deliver values more predictably and incrementally but do not stagnate since they are always refining their operations.
Boost Your Agile Journey with Valuex2.com
The introduction of the SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) hierarchy will revolutionise your organization by facilitating the processes, improving cooperation, and linking with the goals. Successful adoption alone cannot be achieved and needs experts and appropriate materials. This is where Valuex2.com comes in – we are your go-to source for all things SAFe!
What Makes Valuex2.com the Best Place for Your SAFe Requirements?
Advanced level SAFe Training and Certification
When you visit Valuex2.com, you will be able to enrol in several courses that will teach your teams everything you need to know about the SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) hierarchy explained. To prepare your team for successful outcomes from individual to team-level training, to enterprise-level certifications, they have you covered.
Custom-Specific Strategies for SAFe Adoption
Every organization is different and, therefore, every organization becomes different when implementing SAFe. At Valuex2.com, we provide individual solutions for the integration of the SAFe Agile Framework structure, which is important to consider because we understand how you can transform both your business processes and your company.
SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) Hierarchy and Roles
It is necessary to know the list of SAFe roles and their place in the scaling of Agile. The professionals at Valuex2.com explain the SAFe framework levels and elements in detail, so you can get the most out of the framework.
Visit Valuex2 today to find out how they can assist you in the realization of the SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) hierarchy and sustainability. Customize your organization with the valuable components of the SAFe Agile Framework and gain the advantages of better-unified cooperation and a higher speed of work.
Conclusion
The SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) hierarchy aims to apply Agile effectively in big enterprises. SAFe makes it possible to structure the enterprise at four basic levels that include team, program, large solution and the entire portfolio to achieve a common strategic vision of the organization. It is pivotal that organizations appreciate how the structure of SAFe Agile works in that it helps in the possession of a positive collaboration, with high visibility, and flow of value within product delivery to customers.
The SAFe framework described in this article summarises how it can structure and make sense of what might otherwise be rather disorganised attempts at scaling Agile. The fundamental components of the SAFe Agile framework should be examined by organizations that would like to achieve better alignment, improve efficiency, and scale up the quality of their delivery processes.
Overcoming limitations associated with the SAFe framework levels can help develop market-driven strategies and keep strategy development heading in the right direction. It is true that through the usage of the SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) hierarchy, the various enterprises can optimise their potential and hence serve the current evolving market needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. What is the main purpose of SAFe?
Ans. The primary goal of SAFe is to provide a set of rules for working Agile and integrate it into large organizations on different levels. Therefore, utilising the SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) hierarchy to associate the strategy with the execution, enables increased cooperation, the delivery of services, and attaining client satisfaction.
Q. How does SAFe differ from Scrum?
Ans. SAFe unifies Agile across organizational groups and coordinates several teams as it is a single-team-oriented activity. SAFe Agile framework structure also has extra layers such as program and portfolio management that are missing in Scrums making SAFe perfect for big firms.
Q. What industries benefit the most from SAFe?
Ans. Technology, healthcare, finance and manufacturing sectors would gain the most through SaFe roles and hierarchy since they require cross-functional coordination, compliance and effective implementation of large solution systems.
Q. What certifications are available for SAFe?
Ans. SAFe Agilist (SA), SAFe Scrum Master (SSM) and SAFe Program Consultant (SPC) certifications are important since they assist people in grasping the SAFe Agile framework components and assist with large-scale Agile implementation.
Q. What challenges can organizations face when adopting SAFe?
Ans. Technologically managed organizations may also undergo challenges such as resisting change, expensive training, and variation in the perception of the SAFe Agile framework structure. The issue appears to be most sensitive where there is poor leadership communication and commitment.







